Navigating the Malware Matrix: Facing the Ransomware
How Businesses Can Stay Resilient Against Cyber Extortion in 2025
In the complex and ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, ransomware stands out as a particularly disruptive and costly adversary. Think of it as a constantly shifting "malware matrix," where threat actors adapt tactics, exploit vulnerabilities, and target organizations with increasing precision, sophisticated techniques and devastating financial implications.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to navigating the ransomware matrix in 2025, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies to protect your organization from this pervasive threat.
Back to the “Basics”: Understanding Ransomware
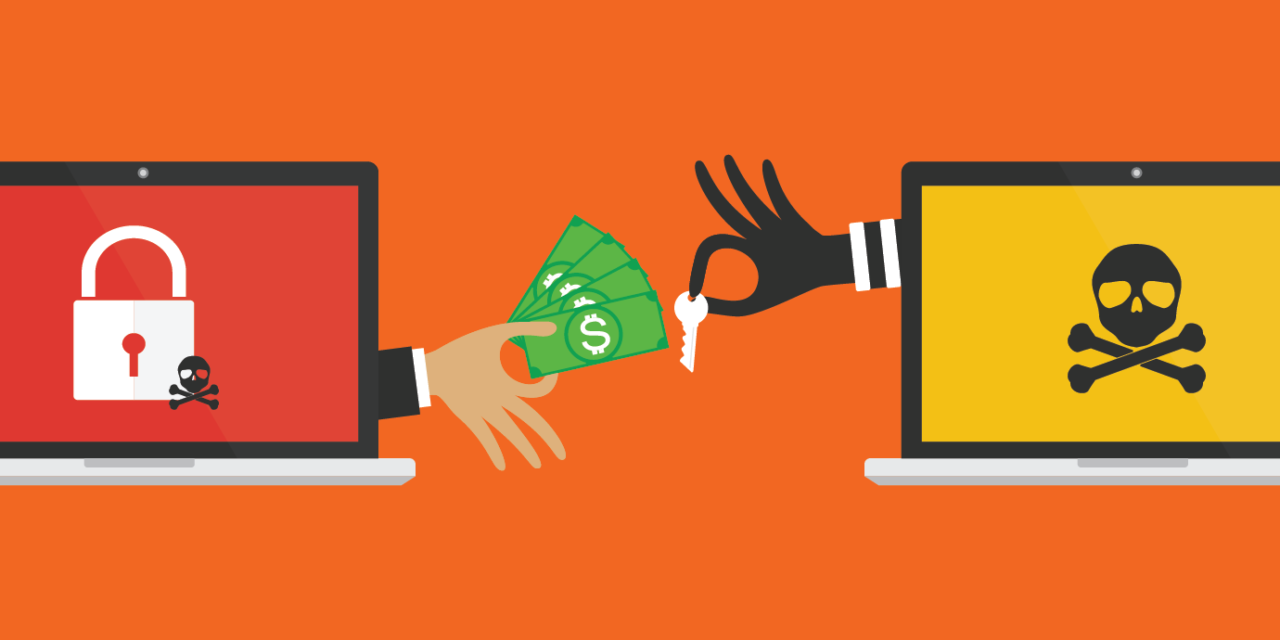
Ransomware is a type of malicious software (malware) that restricts access to a user's system, either by encrypting files or locking the entire system. Attackers then demand a ransom payment, in exchange for restoring access. Modern ransomware have evolved beyond simple encryption, with tactics like double extortion (encrypting data and threatening to leak them to the public) adding extra pressure, particularly for businesses concerned about reputational damage.
The impact of a successful ransomware attack goes far beyond that though: from operational disruptions to significant financial losses, and legal liabilities, these attacks are part of the cutting-edge toolbox at the attacker’s disposal.
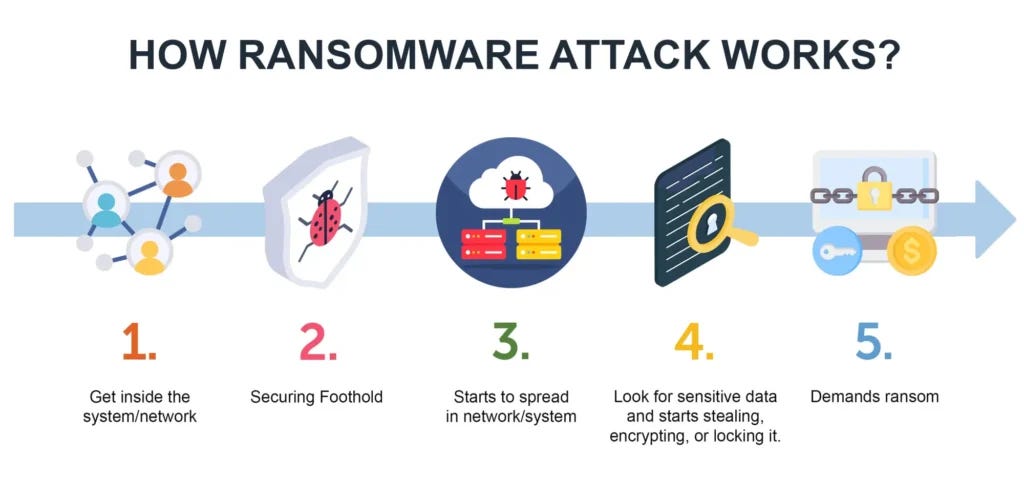
How Ransomware Infections Work: A Five-Stage Process
RECONNAISSANCE & TARGET SELECTION: Attackers research and select organizations to attack, gathering information to identify vulnerabilities and potential avenues for exploitation.
INITIAL ACCESS: Hackers deploy ransomware through various methods, including phishing emails, exploit kits, malvertising, social engineering, drive-by downloads, and remote desktop protocol (RDP) exploits. Phishing attacks, where victims receive emails with malware-ridden attachments, remain the most common method.
LATERAL MOVEMENT AND COMMAND & CONTROL: once inside, attackers navigate the compromised network to locate valuable data, critical systems, and potential targets for encryption at the same time gaining control over multiple machines and use Command & Control (C2) techniques to escalate their privileges.
DEPLOYMENT OF THE PAYLOAD AND ENCRYPTION: attackers deploy the ransomware payload (malicious software that executes harmful actions) encrypting the victim’s files.
EXTORTION: The hacker notifies the user that their system has been compromised. This message includes the ransom amount and instructions on where to send it, often demanding payment in cryptocurrencies, for decryption.
Types of Ransomware: Knowing Your Enemy
Encrypting Ransomware: Encrypts sensitive files, such as documents, videos, and pictures, but does not lock users out of their devices altogether.
Locker Ransomware: Prevents users from accessing their systems and encrypts their files, leading to significant downtime and affecting productivity.
Scareware: Scammers use scareware to deceive users into believing their systems have been infected or compromised. They prompt users to pay fines, only to realize their systems were fine.
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS): A business model where ransomware is sold or leased to criminals (affiliates). This allows individuals with little technical knowledge to launch attacks.
Doxware/Leakware: Hackers threaten to make your data public unless a fine is paid. This type of attack is common among businesses holding sensitive customer data.
2025 Ransomware Trends: What's Changing?
The ransomware landscape in 2025 is marked by increasing frequency, sophistication, and impact, with attacks projected to grow by 53% year-on-year (Trout - State of the Ransomware in 2025 - Report). Several key trends define this evolution.
The number of distinct ransomware groups is expanding at an alarming rate.
Technology and manufacturing remain top targets due to their reliance on interconnected systems and intellectual property, but business services, energy, healthcare, and financial institutions also face persistent threats.
Geographic Hotspots: Over half (51.5%) of all ransomware attacks targeted the United States, with other countries seeing alarming increases.
Attackers are increasingly employing advanced tactics, including encryption-less extortion and exploiting vulnerabilities to maximize impact.
AI is also being leveraged to generate more convincing phishing emails and spread or recode malware.
Recent Ransomware Attack Case Studies
One of the most notable ransomware incidents in recent years involved Clop exploiting vulnerabilities in MOVEit File Transfer software used by over 100 organizations globally. The group gained access via unpatched software flaws, exfiltrated sensitive data, and demanded ransoms under threat of public leaks.
Another example is the famed Akira ransomware, which was initially discovered in March 2023 and has quickly established itself as a major threat to enterprises across numerous industries. Akira operates on a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, allowing affiliates to deploy its ransomware, making it available even to attackers with limited technical knowledge. Akira is known for its sophisticated tactics, which target both Windows and Linux computers, including VMware ESXi virtual machines, and use advanced strategies for persistence, evasion, and extortion.
Other notable ransomware attacks are:
Los Angeles Times (2018): Operations were disrupted by RYUK, an RaaS.
Sony (2014): Systems were compromised, and confidential documents were released using doxware.
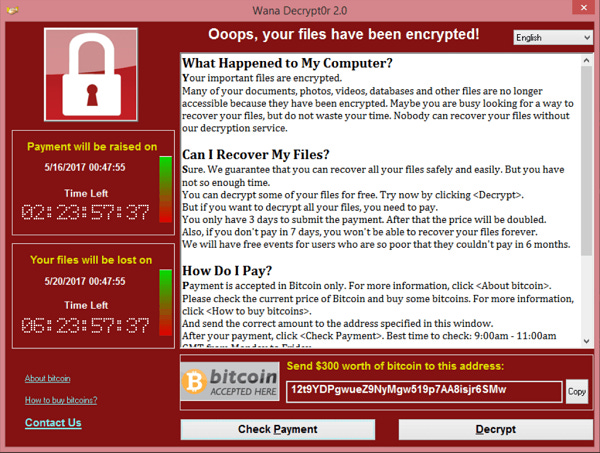
WannaCry (2017): Affected over 230,000 devices in 150 countries (image below)
The Ransomware Recovery Playbook: Minimize Chances and Deal with Them Effectively
Ransomware attacks are no longer a matter of if but when. Preparing today ensures resilience tomorrow, therefore comprehensive prevention strategies and effective response plans can significantly reduce the risk of an attack and mitigate its impact. Let’s see how to minimize the chances of it:
A COMPHRENSIVE BACKUP STRATEGY, with:
REGULAR BACKUPS to ensure business continuity in case of an attack;
OFFLINE STORAGE: storing backups, preferably in air-gapped environments, to prevent ransomware to encrypt them and regularly test for their functionality;
IMPLEMENT ROBUST CYBERSECURITY MEASURES:
STREGHTEN END-POINT SECUITY, with cutting-edge solutions that detects suspicious activity in real time and respond promptly;
ENABLE MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENITCATION (MFA), to prevent unauthorized logins;
NETWORK SEGMENTATION, to limit lateral movements;
ADOPTING A ZERO-TRUST MODEL, assuming no device is trusted by default and verify every access request before granting permission.
LEVERAGE THREAT INTELLIGENCE, stay informed about emerging threats and position your organization ahead of the curve.
DEVELOP A POWERFUL INCIDENT RESPONSE PLAN
and TEST THEM REGULARLY to ensure the backups are complete and usable and the incident response plan can be implemented quickly
TRAINING & DEVELOPING A CYBERSECURITY AWARENESS CULTURE:
SIMULATE PHISHING CAMPAIGNS, conducting regular phishing tests to educate employees about recognizing phishing emails;
CYBER HYGIENE TRAINING, by teaching staff about strong password practices, avoiding suspicious links, and reporting threats promptly.
REPORT THE ATTACK to the right regulatory law enforcement agencies.
Conclusions
Recovery from a ransomware attack is a complex process that involves quick action, meticulous planning, and strong security measures to prevent reinfection. While no system is completely immune to ransomware attacks, being prepared can mean the difference between a minor disruption and a catastrophic event. By following a structured approach—containment, assessment, eradication, recovery—and implementing best practices such as offline backups and incident response plans, organizations can reduce downtime and financial losses while strengthening their defenses against future threats.
Stay ahead of emerging cyber threats by subscribing to my Substack newsletter! You'll get exclusive insights into the latest cybersecurity trends, expert tips on protecting your digital footprint, and early access to in-depth articles like this one—empowering you with knowledge that keeps pace with tomorrow’s challenges today! 📚💻